Nicole Spector
www.nbcnews.com
Originally posted August 5, 2018
Here are two excerpts:
What does therapy mean to you? What areas of your life do you want to explore and how? Do you want to talk about your family, or would you rather focus on a very specific past trauma or would you just like someone to talk with about whatever might be troubling you that week? The answers to these questions may change over time, but when you first go into therapy, ideally you should have some picture of what you want.
“You should know what you want to work on [when beginning therapy],” says Dr. Cira. “Do you feel really strong that you don't want to focus on your past and only the present? Do you want to focus more on things that have happened to you in the past? Do you want someone to help you ‘solve’ your problems or someone who will really sit with you in your pain or both? These are all things you should ask yourself that will help guide your search.”
(cut)
“Listen to your intuition,” says Humphreys. “If you feel instinctively unsafe with a therapist, that will probably inhibit the progress you will make. In contrast, if you feel you ‘click’ with a therapist, that's a good sign that you will be able to build a working alliance with them.”
Jor-El Caraballo, a licensed therapist, wellness coach and co-creator of Viva Wellness, notes that while there are measures that are clinical in nature there is also “a visceral feeling of just being comfortable enough to sit in a room with someone for the therapy hour. That can't be replaced and if you don't feel comfortable enough in a few sessions then it's probably best to tell your therapist this and work toward moving on.”
The info is here.
Welcome to the Nexus of Ethics, Psychology, Morality, Philosophy and Health Care
Welcome to the nexus of ethics, psychology, morality, technology, health care, and philosophy
Monday, September 24, 2018
Distinct Brain Areas involved in Anger versus Punishment during Social Interactions
Olga M. Klimecki, David Sander & Patrik Vuilleumier
Scientific Reports volume 8, Article number: 10556 (2018)
Abstract
Although anger and aggression can have wide-ranging consequences for social interactions, there is sparse knowledge as to which brain activations underlie the feelings of anger and the regulation of related punishment behaviors. To address these issues, we studied brain activity while participants played an economic interaction paradigm called Inequality Game (IG). The current study confirms that the IG elicits anger through the competitive behavior of an unfair (versus fair) other and promotes punishment behavior. Critically, when participants see the face of the unfair other, self-reported anger is parametrically related to activations in temporal areas and amygdala – regions typically associated with mentalizing and emotion processing, respectively. During anger provocation, activations in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, an area important for regulating emotions, predicted the inhibition of later punishment behavior. When participants subsequently engaged in behavioral decisions for the unfair versus fair other, increased activations were observed in regions involved in behavioral adjustment and social cognition, comprising posterior cingulate cortex, temporal cortex, and precuneus. These data point to a distinction of brain activations related to angry feelings and the control of subsequent behavioral choices. Furthermore, they show a contribution of prefrontal control mechanisms during anger provocation to the inhibition of later punishment.
The research is here.
Scientific Reports volume 8, Article number: 10556 (2018)
Abstract
Although anger and aggression can have wide-ranging consequences for social interactions, there is sparse knowledge as to which brain activations underlie the feelings of anger and the regulation of related punishment behaviors. To address these issues, we studied brain activity while participants played an economic interaction paradigm called Inequality Game (IG). The current study confirms that the IG elicits anger through the competitive behavior of an unfair (versus fair) other and promotes punishment behavior. Critically, when participants see the face of the unfair other, self-reported anger is parametrically related to activations in temporal areas and amygdala – regions typically associated with mentalizing and emotion processing, respectively. During anger provocation, activations in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, an area important for regulating emotions, predicted the inhibition of later punishment behavior. When participants subsequently engaged in behavioral decisions for the unfair versus fair other, increased activations were observed in regions involved in behavioral adjustment and social cognition, comprising posterior cingulate cortex, temporal cortex, and precuneus. These data point to a distinction of brain activations related to angry feelings and the control of subsequent behavioral choices. Furthermore, they show a contribution of prefrontal control mechanisms during anger provocation to the inhibition of later punishment.
The research is here.
Sunday, September 23, 2018
The radical moral implications of luck in human life
 David Roberts
David Robertsvox.com
Originally posted August 21, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
So, then, here you are. You turn 18. You are no longer a child; you are an adult, a moral agent, responsible for who you are and what you do.
By that time, your inheritance is enormous. You’ve not only been granted a genetic makeup, an ethnicity and appearance, by accidents of nature and parentage. You’ve also had your latent genetic traits “activated” in a very specific way through a specific upbringing, in a specific environment, with a specific set of experiences.
Your basic mental and emotional wiring is in place; you have certain instincts, predilections, fears, and cravings. You have a certain amount of money, certain social connections and opportunities, a certain family lineage. You’ve had a certain amount and quality of education. You’re a certain kind of person.
You are not responsible for any of that stuff; you weren’t yet capable of being responsible. You were just a kid (or worse, a teen). You didn’t choose your genes or your experiences. Both nature and the vast bulk of the nurture that matters happened to you.
And yet when you turn 18, it’s all yours — the whole inheritance, warts and all. By the time you are an autonomous, responsible moral agent, you have effectively been fired out of a cannon, on a particular trajectory. You wake up, morally speaking, midflight.
The info is here.
Saturday, September 22, 2018
The Business Case for Curiosity
Francesca Gino
Harvard Business Review
Originally posted September-October Issue
Here are two excerpts:
The Benefits of Curiosity
New research reveals a wide range of benefits for organizations, leaders, and employees.
Fewer decision-making errors.
In my research I found that when our curiosity is triggered, we are less likely to fall prey to confirmation bias (looking for information that supports our beliefs rather than for evidence suggesting we are wrong) and to stereotyping people (making broad judgments, such as that women or minorities don’t make good leaders). Curiosity has these positive effects because it leads us to generate alternatives.
(cut)
It’s natural to concentrate on results, especially in the face of tough challenges. But focusing on learning is generally more beneficial to us and our organizations, as some landmark studies show. For example, when U.S. Air Force personnel were given a demanding goal for the number of planes to be landed in a set time frame, their performance decreased. Similarly, in a study led by Southern Methodist University’s Don VandeWalle, sales professionals who were naturally focused on performance goals, such as meeting their targets and being seen by colleagues as good at their jobs, did worse during a promotion of a product (a piece of medical equipment priced at about $5,400) than reps who were naturally focused on learning goals, such as exploring how to be a better salesperson. That cost them, because the company awarded a bonus of $300 for each unit sold.
A body of research demonstrates that framing work around learning goals (developing competence, acquiring skills, mastering new situations, and so on) rather than performance goals (hitting targets, proving our competence, impressing others) boosts motivation. And when motivated by learning goals, we acquire more-diverse skills, do better at work, get higher grades in college, do better on problem-solving tasks, and receive higher ratings after training. Unfortunately, organizations often prioritize performance goals.
The information is here.
Harvard Business Review
Originally posted September-October Issue
Here are two excerpts:
The Benefits of Curiosity
New research reveals a wide range of benefits for organizations, leaders, and employees.
Fewer decision-making errors.
In my research I found that when our curiosity is triggered, we are less likely to fall prey to confirmation bias (looking for information that supports our beliefs rather than for evidence suggesting we are wrong) and to stereotyping people (making broad judgments, such as that women or minorities don’t make good leaders). Curiosity has these positive effects because it leads us to generate alternatives.
(cut)
It’s natural to concentrate on results, especially in the face of tough challenges. But focusing on learning is generally more beneficial to us and our organizations, as some landmark studies show. For example, when U.S. Air Force personnel were given a demanding goal for the number of planes to be landed in a set time frame, their performance decreased. Similarly, in a study led by Southern Methodist University’s Don VandeWalle, sales professionals who were naturally focused on performance goals, such as meeting their targets and being seen by colleagues as good at their jobs, did worse during a promotion of a product (a piece of medical equipment priced at about $5,400) than reps who were naturally focused on learning goals, such as exploring how to be a better salesperson. That cost them, because the company awarded a bonus of $300 for each unit sold.
A body of research demonstrates that framing work around learning goals (developing competence, acquiring skills, mastering new situations, and so on) rather than performance goals (hitting targets, proving our competence, impressing others) boosts motivation. And when motivated by learning goals, we acquire more-diverse skills, do better at work, get higher grades in college, do better on problem-solving tasks, and receive higher ratings after training. Unfortunately, organizations often prioritize performance goals.
The information is here.
Friday, September 21, 2018
Surprised By A Medical Bill? Join The Club. Most Americans Say They Have Been
Alison Kodjak
www.npr.org
Originally posted September 2, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Most survey respondents — 57 percent — have been surprised by a medical bill they thought would be paid for by their insurance companies, the survey from the research group NORC at the University of Chicago finds.
"People get surprised by all kinds of bills, for all kinds of reasons," says Caroline Pearson, a senior fellow at NORC.
Pearson herself says she was not expecting the problem to be so widespread.
The survey shows that 53 percent of those surveyed were surprised by a bill for a physician's service, and 51 percent got an unexpected bill for a laboratory test – like the urine test featured in our earlier story.
Hospital and health care facility charges surprised 43 percent of respondents, and 35 percent reported getting unexpected bills for imaging services, like the CT scan featured by NPR.
The survey shows that while some of the unexpected bills come because doctors or hospitals where patients are treated don't participate in the patients' insurance networks, the majority come because patients expect their insurance to cover more than it actually does.
The info is here.
www.npr.org
Originally posted September 2, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Most survey respondents — 57 percent — have been surprised by a medical bill they thought would be paid for by their insurance companies, the survey from the research group NORC at the University of Chicago finds.
"People get surprised by all kinds of bills, for all kinds of reasons," says Caroline Pearson, a senior fellow at NORC.
Pearson herself says she was not expecting the problem to be so widespread.
The survey shows that 53 percent of those surveyed were surprised by a bill for a physician's service, and 51 percent got an unexpected bill for a laboratory test – like the urine test featured in our earlier story.
Hospital and health care facility charges surprised 43 percent of respondents, and 35 percent reported getting unexpected bills for imaging services, like the CT scan featured by NPR.
The survey shows that while some of the unexpected bills come because doctors or hospitals where patients are treated don't participate in the patients' insurance networks, the majority come because patients expect their insurance to cover more than it actually does.
The info is here.
Why Social Science Needs Evolutionary Theory
Christine Legare
Nautilus.com
Originally posted June 15, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Human cognition and behavior is the product of the interaction of genetic and cultural evolution. Gene-culture co-evolution has allowed us to adapt to highly diverse ecologies and to produce cultural adaptations and innovations. It has also produced extraordinary cultural diversity. In fact, cultural variability is one of our species’ most distinctive features. Humans display a wider repertoire of behaviors that vary more within and across groups than any other animal. Social learning enables cultural transmission, so the psychological mechanisms supporting it should be universal. These psychological mechanisms must also be highly responsive to diverse developmental contexts and cultural ecologies.
Take the conformity bias. It is a universal proclivity of all human psychology—even very young children imitate the behavior of others and conform to group norms. Yet beliefs about conformity vary substantially between populations. Adults in some populations are more likely to associate conformity with children’s intelligence, whereas others view creative non-conformity as linked with intelligence. Psychological adaptations for social learning, such as conformity bias, develop in complex and diverse cultural ecologies that work in tandem to shape the human mind and generate cultural variation.
The info is here.
Nautilus.com
Originally posted June 15, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Human cognition and behavior is the product of the interaction of genetic and cultural evolution. Gene-culture co-evolution has allowed us to adapt to highly diverse ecologies and to produce cultural adaptations and innovations. It has also produced extraordinary cultural diversity. In fact, cultural variability is one of our species’ most distinctive features. Humans display a wider repertoire of behaviors that vary more within and across groups than any other animal. Social learning enables cultural transmission, so the psychological mechanisms supporting it should be universal. These psychological mechanisms must also be highly responsive to diverse developmental contexts and cultural ecologies.
Take the conformity bias. It is a universal proclivity of all human psychology—even very young children imitate the behavior of others and conform to group norms. Yet beliefs about conformity vary substantially between populations. Adults in some populations are more likely to associate conformity with children’s intelligence, whereas others view creative non-conformity as linked with intelligence. Psychological adaptations for social learning, such as conformity bias, develop in complex and diverse cultural ecologies that work in tandem to shape the human mind and generate cultural variation.
The info is here.
Thursday, September 20, 2018
Man-made human 'minibrains' spark debate on ethics and morality
Carolyn Y. Johnson
www.iol.za
Originally posted September 3, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Five years ago, an ethical debate about organoids seemed to many scientists to be premature. The organoids were exciting because they were similar to the developing brain, and yet they were incredibly rudimentary. They were constrained in how big they could get before cells in the core started dying, because they weren't suffused with blood vessels or supplied with nutrients and oxygen by a beating heart. They lacked key cell types.
Still, there was something different about brain organoids compared with routine biomedical research. Song recalled that one of the amazing but also unsettling things about the early organoids was that they weren't as targeted to develop into specific regions of the brain, so it was possible to accidentally get retinal cells.
"It's difficult to see the eye in a dish," Song said.
Now, researchers are succeeding at keeping organoids alive for longer periods of time. At a talk, Hyun recalled one researcher joking that the lab had sung "Happy Birthday" to an organoid when it was a year old. Some researchers are implanting organoids into rodent brains, where they can stay alive longer and grow more mature. Others are building multiple organoids representing different parts of the brain, such as the hippocampus, which is involved in memory, or the cerebral cortex - the seat of cognition - and fusing them together into larger "assembloids."
Even as scientists express scepticism that brain organoids will ever come close to sentience, they're the ones calling for a broad discussion, and perhaps more oversight. The questions range from the practical to the fantastical. Should researchers make sure that people who donate their cells for organoid research are informed that they could be used to make a tiny replica of parts of their brain? If organoids became sophisticated enough, should they be granted greater protections, like the rules that govern animal research? Without a consensus on what consciousness or pain would even look like in the brain, how will scientists know when they're nearing the limit?
The info is here.
www.iol.za
Originally posted September 3, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Five years ago, an ethical debate about organoids seemed to many scientists to be premature. The organoids were exciting because they were similar to the developing brain, and yet they were incredibly rudimentary. They were constrained in how big they could get before cells in the core started dying, because they weren't suffused with blood vessels or supplied with nutrients and oxygen by a beating heart. They lacked key cell types.
Still, there was something different about brain organoids compared with routine biomedical research. Song recalled that one of the amazing but also unsettling things about the early organoids was that they weren't as targeted to develop into specific regions of the brain, so it was possible to accidentally get retinal cells.
"It's difficult to see the eye in a dish," Song said.
Now, researchers are succeeding at keeping organoids alive for longer periods of time. At a talk, Hyun recalled one researcher joking that the lab had sung "Happy Birthday" to an organoid when it was a year old. Some researchers are implanting organoids into rodent brains, where they can stay alive longer and grow more mature. Others are building multiple organoids representing different parts of the brain, such as the hippocampus, which is involved in memory, or the cerebral cortex - the seat of cognition - and fusing them together into larger "assembloids."
Even as scientists express scepticism that brain organoids will ever come close to sentience, they're the ones calling for a broad discussion, and perhaps more oversight. The questions range from the practical to the fantastical. Should researchers make sure that people who donate their cells for organoid research are informed that they could be used to make a tiny replica of parts of their brain? If organoids became sophisticated enough, should they be granted greater protections, like the rules that govern animal research? Without a consensus on what consciousness or pain would even look like in the brain, how will scientists know when they're nearing the limit?
The info is here.
John Rawls’ ‘A Theory of Justice’
Ben Davis
1000-Word Philosophy
Originally posted July 27, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Reasonable people often disagree about how to live, but we need to structure society in a way that reasonable members of that society can accept. Citizens could try to collectively agree on basic rules. We needn’t decide every detail: we might only worry about rules concerning major political and social institutions, like the legal system and economy, which form the ‘basic structure’ of society.
A collective agreement on the basic structure of society is an attractive ideal. But some people are more powerful than others: some may be wealthier, or part of a social majority. If people can dominate negotiations because of qualities that are, as Rawls (72-75) puts it, morally arbitrary, that is wrong. People don’t earn these advantages: they get them by luck. For anyone to use these unearned advantages to their own benefit is unfair, and the source of many injustices.
This inspires Rawls’ central claim that we should conceive of justice ‘as fairness.’ To identify fairness, Rawls (120) develops two important concepts: the original position and the veil of ignorance:
The original position is a hypothetical situation: Rawls asks what social rules and institutions people would agree to, not in an actual discussion, but under fair conditions, where nobody knows whether they are advantaged by luck. Fairness is achieved through the veil of ignorance, an imagined device where the people choosing the basic structure of society (‘deliberators’) have morally arbitrary features hidden from them: since they have no knowledge of these features, any decision they make can’t be biased in their own favour.
The brief, excellent synopsis is here.
1000-Word Philosophy
Originally posted July 27, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Reasonable people often disagree about how to live, but we need to structure society in a way that reasonable members of that society can accept. Citizens could try to collectively agree on basic rules. We needn’t decide every detail: we might only worry about rules concerning major political and social institutions, like the legal system and economy, which form the ‘basic structure’ of society.
A collective agreement on the basic structure of society is an attractive ideal. But some people are more powerful than others: some may be wealthier, or part of a social majority. If people can dominate negotiations because of qualities that are, as Rawls (72-75) puts it, morally arbitrary, that is wrong. People don’t earn these advantages: they get them by luck. For anyone to use these unearned advantages to their own benefit is unfair, and the source of many injustices.
This inspires Rawls’ central claim that we should conceive of justice ‘as fairness.’ To identify fairness, Rawls (120) develops two important concepts: the original position and the veil of ignorance:
The original position is a hypothetical situation: Rawls asks what social rules and institutions people would agree to, not in an actual discussion, but under fair conditions, where nobody knows whether they are advantaged by luck. Fairness is achieved through the veil of ignorance, an imagined device where the people choosing the basic structure of society (‘deliberators’) have morally arbitrary features hidden from them: since they have no knowledge of these features, any decision they make can’t be biased in their own favour.
The brief, excellent synopsis is here.
Wednesday, September 19, 2018
Why “happy” doctors die by suicide
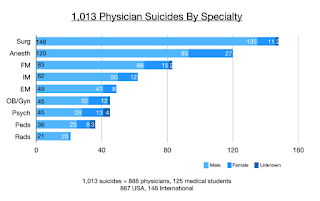 Pamela Wible
Pamela Wiblewww.idealmedicalcare.org
Originally posted on August 24, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Doctor suicides on the registry were submitted to me during a six-year period (2012-2018) by families, friends, and colleagues who knew the deceased. After speaking to thousands of suicidal physicians since 2012 on my informal doctor suicide hotline and analyzing registry data, I discovered surprising themes—many unique to physicians.
Public perception maintains that doctors are successful, intelligent, wealthy, and immune from the problems of the masses. To patients, it is inconceivable that doctors would have the highest suicide rate of any profession (5).
Even more baffling, “happy” doctors are dying by suicide. Many doctors who kill themselves appear to be the most optimistic, upbeat, and confident people. Just back from Disneyland, just bought tickets for a family cruise, just gave a thumbs up to the team after a successful surgery—and hours later they shoot themselves in the head.
Doctors are masters of disguise and compartmentalization.
Turns out some of the happiest people—especially those who spend their days making other people happy—may be masking their own despair.
The info is here.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

