Bradley Belsher, Derek Smolenski, Larry Pruitt, and others
JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(6):642-651.
doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0174
Abstract
Importance Suicide prediction models have the potential to improve the identification of patients at heightened suicide risk by using predictive algorithms on large-scale data sources. Suicide prediction models are being developed for use across enterprise-level health care systems including the US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs, and Kaiser Permanente.
Objectives
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of suicide prediction models in predicting suicide and suicide attempts and to simulate the effects of implementing suicide prediction models using population-level estimates of suicide rates.
Evidence Review
A systematic literature search was conducted in MEDLINE, PsycINFO, Embase, and the Cochrane Library to identify research evaluating the predictive accuracy of suicide prediction models in identifying patients at high risk for a suicide attempt or death by suicide. Each database was searched from inception to August 21, 2018. The search strategy included search terms for suicidal behavior, risk prediction, and predictive modeling. Reference lists of included studies were also screened. Two reviewers independently screened and evaluated eligible studies.
Findings
From a total of 7306 abstracts reviewed, 17 cohort studies met the inclusion criteria, representing 64 unique prediction models across 5 countries with more than 14 million participants. The research quality of the included studies was generally high. Global classification accuracy was good (≥0.80 in most models), while the predictive validity associated with a positive result for suicide mortality was extremely low (≤0.01 in most models). Simulations of the results suggest very low positive predictive values across a variety of population assessment characteristics.
Conclusions and Relevance
To date, suicide prediction models produce accurate overall classification models, but their accuracy of predicting a future event is near 0. Several critical concerns remain unaddressed, precluding their readiness for clinical applications across health systems.
Welcome to the Nexus of Ethics, Psychology, Morality, Philosophy and Health Care
Welcome to the nexus of ethics, psychology, morality, technology, health care, and philosophy
Showing posts with label Suicide. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Suicide. Show all posts
Monday, July 8, 2019
Wednesday, July 3, 2019
U.S. Suicide Rates Are the Highest They've Been Since World War II
 Jamie Ducharme
Jamie DucharmeTime.com
Originally posted June 20, 2019
U.S. suicide rates are at their highest since World War II, according to federal data—and the opioid crisis, widespread social media use and high rates of stress may be among the myriad contributing factors.
In 2017, 14 out of every 100,000 Americans died by suicide, according to a new analysis released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics. That’s a 33% increase since 1999, and the highest age-adjusted suicide rate recorded in the U.S. since 1942. (Rates were even higher during the Great Depression, hitting a century peak of 21.9 in 1932.)
“I don’t think there’s a one-size-fits all reason” since there’s almost never a single cause of suicide, says Jill Harkavy-Friedman, vice president of research at the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, a nonprofit that supports suicide prevention research, education and policy. “I don’t think there’s something you can pinpoint, but I do think a period of increased stress and a lack of a sense of security may be contributing.”
It’s even more difficult to assign causes to the uptick, Harkavy-Friedman says, because it’s happening across diverse demographic groups. Men have historically died by suicide more frequently than women, and that’s still true: As of 2017, the male suicide rate was more than three times higher than the female rate. But female suicide rates are rising more quickly—by 53% since 1999, compared to 26% for men—and the gap is narrowing. For both genders, suicide rates are highest among American Indians and Alaska natives, compared to other ethnicities, and when the data are broken down by age group, the most suicide deaths are reported among people ages 45 to 64—but nearly every ethnic and age group saw an increase of some size from 1999 to 2017.
The info is here.
Friday, May 17, 2019
More than 300 overworked NHS nurses have died by suicide in just seven years
 Alan Selby
Alan SelbyThe Mirror
Originally posted April 27, 2019
More than 300 nurses have taken their own lives in just seven years, shocking new figures reveal.
During the worst year, one was dying by suicide EVERY WEEK as Tory cuts began to bite deep into the NHS.
Today victims’ families call for vital early mental health training and support for young nurses – and an end to a “bullying and toxic culture” in the health service which leaves them afraid to ask for help in their darkest moments.
One mum – whose trainee nurse daughter Lucy de Oliveira killed herself while juggling other jobs to make ends meet – told us: “They’re working all hours God sends doing a really important job. Most of them would be better off working in McDonald’s. That can’t be right.”
Shadow Health Secretary Jonathan Ashworth has called for a government inquiry into the “alarming” figures – 23 per cent higher than the national average – from 2011 to 2017, the latest year on record.
“Every life lost is a desperate tragedy,” he said. “The health and wellbeing of NHS staff must never be compromised.”
The info is here.
Friday, April 5, 2019
A Prominent Economist’s Death Prompts Talk of Mental Health in the Professoriate
Emma Pettit
The Chronicle of Higher Education
Originally posted March 19, 2019
Reaching Out
For Bruce Macintosh, Krueger’s death was a reminder of how isolating academe can be. Macintosh is a professor of physics at Stanford University who was employed at a national laboratory, not a university, until about five years ago. That culture was totally different, he said. At other workplaces, Macintosh said, you interact regularly with peers and supervisors, who are paying close attention to you and your work.
“There’s nothing like that in an academic environment,” he said. “You can shut down completely for a year, and no one will notice,” as long as the grades get turned in.
It seems, Macintosh said, as if there should be multiple layers of support within a university department to help faculty members who experience depression or other forms of mental illness. But certain barriers still exist between professors and the resources they need.
A 2017 survey of 267 faculty members with mental-health histories or mental illnesses found that most respondents had little to no familiarity with accommodations at their institution. Even fewer reported using them.
The info is here.
Note: Career success, wealth, and prestige are not protective factors for suicide attempts or completions. Interpersonal connections to family and friends, access to quality mental health care, problem-solving skills, meaning in life, and purposefulness are.
The Chronicle of Higher Education
Originally posted March 19, 2019
Reaching Out
For Bruce Macintosh, Krueger’s death was a reminder of how isolating academe can be. Macintosh is a professor of physics at Stanford University who was employed at a national laboratory, not a university, until about five years ago. That culture was totally different, he said. At other workplaces, Macintosh said, you interact regularly with peers and supervisors, who are paying close attention to you and your work.
“There’s nothing like that in an academic environment,” he said. “You can shut down completely for a year, and no one will notice,” as long as the grades get turned in.
It seems, Macintosh said, as if there should be multiple layers of support within a university department to help faculty members who experience depression or other forms of mental illness. But certain barriers still exist between professors and the resources they need.
A 2017 survey of 267 faculty members with mental-health histories or mental illnesses found that most respondents had little to no familiarity with accommodations at their institution. Even fewer reported using them.
The info is here.
Note: Career success, wealth, and prestige are not protective factors for suicide attempts or completions. Interpersonal connections to family and friends, access to quality mental health care, problem-solving skills, meaning in life, and purposefulness are.
Monday, March 11, 2019
The Parking Lot Suicide
Emily Wax-Thibodeaux.
The Washington Post
Originally published February 11, 2019
Here is an excerpt:
Miller was suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder and suicidal thoughts when he checked into the Minneapolis Department of Veterans Affairs hospital in February 2018. After spending four days in the mental-health unit, Miller walked to his truck in VA’s parking lot and shot himself in the very place he went to find help.
“The fact that my brother, Justin, never left the VA parking lot — it’s infuriating,” said Harrington, 37. “He did the right thing; he went in for help. I just can’t get my head around it.”
A federal investigation into Miller’s death found that the Minneapolis VA made multiple errors: not scheduling a follow-up appointment, failing to communicate with his family about the treatment plan and inadequately assessing his access to firearms.
Several days after his death, Miller’s parents received a package from the Department of Veterans Affairs — bottles of antidepressants and sleep aids prescribed to Miller.
His death is among 19 suicides that occurred on VA campuses from October 2017 to November 2018, seven of them in parking lots, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs.
While studies show that every suicide is highly complex — influenced by genetics, financial uncertainty, relationship loss and other factors — mental-health experts worry that veterans taking their lives on VA property has become a desperate form of protest against a system that some veterans feel hasn’t helped them.
The most recent parking lot suicide occurred weeks before Christmas in St. Petersburg, Fla. Marine Col. Jim Turner, 55, dressed in his uniform blues and medals, sat on top of his military and VA records and killed himself with a rifle outside the Bay Pines Department of Veterans Affairs.
“I bet if you look at the 22 suicides a day you will see VA screwed up in 90%,” Turner wrote in a note investigators found near his body.
The info is here.
The Washington Post
Originally published February 11, 2019
Here is an excerpt:
Miller was suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder and suicidal thoughts when he checked into the Minneapolis Department of Veterans Affairs hospital in February 2018. After spending four days in the mental-health unit, Miller walked to his truck in VA’s parking lot and shot himself in the very place he went to find help.
“The fact that my brother, Justin, never left the VA parking lot — it’s infuriating,” said Harrington, 37. “He did the right thing; he went in for help. I just can’t get my head around it.”
A federal investigation into Miller’s death found that the Minneapolis VA made multiple errors: not scheduling a follow-up appointment, failing to communicate with his family about the treatment plan and inadequately assessing his access to firearms.
Several days after his death, Miller’s parents received a package from the Department of Veterans Affairs — bottles of antidepressants and sleep aids prescribed to Miller.
His death is among 19 suicides that occurred on VA campuses from October 2017 to November 2018, seven of them in parking lots, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs.
While studies show that every suicide is highly complex — influenced by genetics, financial uncertainty, relationship loss and other factors — mental-health experts worry that veterans taking their lives on VA property has become a desperate form of protest against a system that some veterans feel hasn’t helped them.
The most recent parking lot suicide occurred weeks before Christmas in St. Petersburg, Fla. Marine Col. Jim Turner, 55, dressed in his uniform blues and medals, sat on top of his military and VA records and killed himself with a rifle outside the Bay Pines Department of Veterans Affairs.
“I bet if you look at the 22 suicides a day you will see VA screwed up in 90%,” Turner wrote in a note investigators found near his body.
The info is here.
Monday, March 4, 2019
Suicide rates at a record high, yet insurers still deny care
Patrick Kennedy and Jim Ramstad
thehill.com
Originally posted February 15, 2019
Here is an excerpt:
A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reinforces the seriousness of our nation’s mental health crisis. Life expectancy is declining in a way we haven’t seen since World War. With more than 70,000 drug overdose deaths in 2017 and suicides increasing by 33 percent since 1999, the message is clear: People are not getting the care they need. And for many, it’s a simple matter of access.
When the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act, also known as the Federal Parity Law, passed in 2008, those of us who drafted and championed the bill knew that talking about mental health wasn’t enough — we needed to ensure access to care as well. Hence, the Federal Parity Law requires most insurers to cover illnesses of the brain, such as depression or addiction, no more restrictively than illnesses of the body, such as diabetes or cancer. We hoped it would remove the barriers that families like Sylvia’s often face when trying to get help.
It has been 10 years since the law passed and, unfortunately, too many Americans are still being denied coverage for mental health and addiction treatment. The reason? A lack of enforcement.
As things stand, the responsibility to challenge inadequate systems of care and illegal denials falls on patients, who are typically unaware of the law or are in the middle of a personal crisis. This isn’t right. Or sustainable. The responsibility for mental health equity should lie with insurers, not with patients or their providers. Insurers should be held accountable for parity before plans are sold.
The info is here.
thehill.com
Originally posted February 15, 2019
Here is an excerpt:
A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reinforces the seriousness of our nation’s mental health crisis. Life expectancy is declining in a way we haven’t seen since World War. With more than 70,000 drug overdose deaths in 2017 and suicides increasing by 33 percent since 1999, the message is clear: People are not getting the care they need. And for many, it’s a simple matter of access.
When the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act, also known as the Federal Parity Law, passed in 2008, those of us who drafted and championed the bill knew that talking about mental health wasn’t enough — we needed to ensure access to care as well. Hence, the Federal Parity Law requires most insurers to cover illnesses of the brain, such as depression or addiction, no more restrictively than illnesses of the body, such as diabetes or cancer. We hoped it would remove the barriers that families like Sylvia’s often face when trying to get help.
It has been 10 years since the law passed and, unfortunately, too many Americans are still being denied coverage for mental health and addiction treatment. The reason? A lack of enforcement.
As things stand, the responsibility to challenge inadequate systems of care and illegal denials falls on patients, who are typically unaware of the law or are in the middle of a personal crisis. This isn’t right. Or sustainable. The responsibility for mental health equity should lie with insurers, not with patients or their providers. Insurers should be held accountable for parity before plans are sold.
The info is here.
Wednesday, December 12, 2018
Why Are Doctors Killing Themselves?
The Practical Professional in Healthcare
October/November 2018
Here is an excerpt:
The nation loses 300 to 400 physicians each year, the equivalent of two large medical school classes, and more than a million patients lose their doctor. According to a new research study encompassing data from the past ten years, physicians are committing suicide at a rate that’s more than twice as high as the average population—higher even than for veterans.
With a critical shortage of physicians looming and advocates like Pamela Wible calling attention to the problem, the increasingly urgent question remains: Why are doctors killing themselves? And what can be done to help? In response, researchers are ramping up their efforts to understand the causes of
physician suicide; leading hospitals, medical schools and professional organizations are pioneering new programs and interventions; and regulators are reconsidering how they might revise the licensing/renewal process to support their efforts.
The info is here.
There are several other articles on physician self-care, which applies to other helping professions.
October/November 2018
Here is an excerpt:
The nation loses 300 to 400 physicians each year, the equivalent of two large medical school classes, and more than a million patients lose their doctor. According to a new research study encompassing data from the past ten years, physicians are committing suicide at a rate that’s more than twice as high as the average population—higher even than for veterans.
With a critical shortage of physicians looming and advocates like Pamela Wible calling attention to the problem, the increasingly urgent question remains: Why are doctors killing themselves? And what can be done to help? In response, researchers are ramping up their efforts to understand the causes of
physician suicide; leading hospitals, medical schools and professional organizations are pioneering new programs and interventions; and regulators are reconsidering how they might revise the licensing/renewal process to support their efforts.
The info is here.
There are several other articles on physician self-care, which applies to other helping professions.
Friday, September 28, 2018
A Debate Over ‘Rational Suicide’
Paula Span
The New York Times
Originally posted August 31, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Is suicide by older adults ever a rational choice? It’s a topic many older people discuss among themselves, quietly or loudly — and one that physicians increasingly encounter, too. Yet most have scant training or experience in how to respond, said Dr. Meera Balasubramaniam, a geriatric psychiatrist at the New York University School of Medicine.
“I found myself coming across individuals who were very old, doing well, and shared that they wanted to end their lives at some point,” said Dr. Balasubramaniam. “So many of our patients are confronting this in their heads.”
She has not taken a position on whether suicide can be rational — her views are “evolving,” she said. But hoping to generate more medical discussion, she and a co-editor explored the issue in a 2017 anthology, “Rational Suicide in the Elderly,” and she revisited it recently in an article in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
The Hastings Center, the ethics institute in Garrison, N.Y., also devoted much of its latest Hastings Center Report to a debate over “voluntary death” to forestall dementia.
Every part of this idea, including the very phrase “rational suicide,” remains intensely controversial. (Let’s leave aside the related but separate issue of physician aid in dying, currently legal in seven states and the District of Columbia, which applies only to mentally competent people likely to die of a terminal illness within six months.)
The info is here.
The New York Times
Originally posted August 31, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Is suicide by older adults ever a rational choice? It’s a topic many older people discuss among themselves, quietly or loudly — and one that physicians increasingly encounter, too. Yet most have scant training or experience in how to respond, said Dr. Meera Balasubramaniam, a geriatric psychiatrist at the New York University School of Medicine.
“I found myself coming across individuals who were very old, doing well, and shared that they wanted to end their lives at some point,” said Dr. Balasubramaniam. “So many of our patients are confronting this in their heads.”
She has not taken a position on whether suicide can be rational — her views are “evolving,” she said. But hoping to generate more medical discussion, she and a co-editor explored the issue in a 2017 anthology, “Rational Suicide in the Elderly,” and she revisited it recently in an article in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
The Hastings Center, the ethics institute in Garrison, N.Y., also devoted much of its latest Hastings Center Report to a debate over “voluntary death” to forestall dementia.
Every part of this idea, including the very phrase “rational suicide,” remains intensely controversial. (Let’s leave aside the related but separate issue of physician aid in dying, currently legal in seven states and the District of Columbia, which applies only to mentally competent people likely to die of a terminal illness within six months.)
The info is here.
Tuesday, September 25, 2018
Doctors’ mental health at tipping point
Chris Hemmings
BBC.co.uk
Originally posted September 3, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
'Last taboo'
Dr Gerada says the lack of confidentiality is a barrier and wants NHS England to extend the London approach to any doctor who needs support.
She believes acknowledging that doctors also have mental health problems is "the last taboo in the NHS".
Louise Freeman, a consultant in emergency medicine, says she left her job after she felt she could not access appropriate support for her depression.
"On the surface you might think 'Oh, doctors will get great mental health care because they'll know who to go to'.
"But actually we're kind of a hard-to-reach group. We can be quite worried about confidentiality," she said, adding that she believes doctors are afraid of coming forwards in case they lose their jobs.
"I was absolutely desperate to stay at work. I never wavered from that."
One of the biggest issues, according to Dr Gerada, is the effect on doctors of complaints from the public, which she says can "shatter their sense of self".
The info is here.
BBC.co.uk
Originally posted September 3, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
'Last taboo'
Dr Gerada says the lack of confidentiality is a barrier and wants NHS England to extend the London approach to any doctor who needs support.
She believes acknowledging that doctors also have mental health problems is "the last taboo in the NHS".
Louise Freeman, a consultant in emergency medicine, says she left her job after she felt she could not access appropriate support for her depression.
"On the surface you might think 'Oh, doctors will get great mental health care because they'll know who to go to'.
"But actually we're kind of a hard-to-reach group. We can be quite worried about confidentiality," she said, adding that she believes doctors are afraid of coming forwards in case they lose their jobs.
"I was absolutely desperate to stay at work. I never wavered from that."
One of the biggest issues, according to Dr Gerada, is the effect on doctors of complaints from the public, which she says can "shatter their sense of self".
The info is here.
Wednesday, September 19, 2018
Why “happy” doctors die by suicide
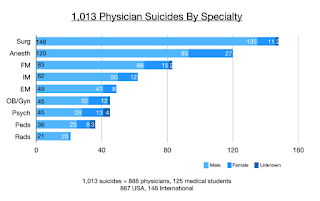 Pamela Wible
Pamela Wiblewww.idealmedicalcare.org
Originally posted on August 24, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Doctor suicides on the registry were submitted to me during a six-year period (2012-2018) by families, friends, and colleagues who knew the deceased. After speaking to thousands of suicidal physicians since 2012 on my informal doctor suicide hotline and analyzing registry data, I discovered surprising themes—many unique to physicians.
Public perception maintains that doctors are successful, intelligent, wealthy, and immune from the problems of the masses. To patients, it is inconceivable that doctors would have the highest suicide rate of any profession (5).
Even more baffling, “happy” doctors are dying by suicide. Many doctors who kill themselves appear to be the most optimistic, upbeat, and confident people. Just back from Disneyland, just bought tickets for a family cruise, just gave a thumbs up to the team after a successful surgery—and hours later they shoot themselves in the head.
Doctors are masters of disguise and compartmentalization.
Turns out some of the happiest people—especially those who spend their days making other people happy—may be masking their own despair.
The info is here.
Friday, September 14, 2018
Law, Ethics, and Conversations between Physicians and Patients about Firearms in the Home
Alexander D. McCourt, and Jon S. Vernick
AMA J Ethics. 2018;20(1):69-76.
Abstract
Firearms in the home pose a risk to household members, including homicide, suicide, and unintentional deaths. Medical societies urge clinicians to counsel patients about those risks as part of sound medical practice. Depending on the circumstances, clinicians might recommend safe firearm storage, temporary removal of the firearm from the home, or other measures. Certain state firearm laws, however, might present legal and ethical challenges for physicians who counsel patients about guns in the home. Specifically, we discuss state background check laws for gun transfers, safe gun storage laws, and laws forbidding physicians from engaging in certain firearm-related conversations with their patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these and other state gun laws but should offer anticipatory guidance when clinically appropriate.
The info is here.
AMA J Ethics. 2018;20(1):69-76.
Abstract
Firearms in the home pose a risk to household members, including homicide, suicide, and unintentional deaths. Medical societies urge clinicians to counsel patients about those risks as part of sound medical practice. Depending on the circumstances, clinicians might recommend safe firearm storage, temporary removal of the firearm from the home, or other measures. Certain state firearm laws, however, might present legal and ethical challenges for physicians who counsel patients about guns in the home. Specifically, we discuss state background check laws for gun transfers, safe gun storage laws, and laws forbidding physicians from engaging in certain firearm-related conversations with their patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these and other state gun laws but should offer anticipatory guidance when clinically appropriate.
The info is here.
Thursday, September 6, 2018
When Doctors Struggle With Suicide, Their Profession Often Fails Them
Blake Farmer
NPR.org
Originally posted July 31, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
A particular danger for doctors trying to fend off suicidal urges is that they know exactly how to end their own lives and often have easy access to the means.
Wenger remembers his friend and colleague as the confident professional with whom he had worked in emergency rooms all over Knoxville — including the one where she died. That day three years ago still makes no sense to him.
"She was very strong-willed, strong-minded, an independent, young, female physician," says emergency doctor Betsy Hull, a close friend. "I don't think any of us had any idea that she was struggling as much personally as she was for those several months."
That day she became part of a grim set of statistics.
A harsh reality
An estimated 300 to 400 doctors kill themselves each year, a rate of 28 to 40 per 100,000 or more than double that of general population. That is according to a review of 10 years of literature on the subject presented at the American Psychiatry Association annual meeting in May.
The information is here.
NPR.org
Originally posted July 31, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
A particular danger for doctors trying to fend off suicidal urges is that they know exactly how to end their own lives and often have easy access to the means.
Wenger remembers his friend and colleague as the confident professional with whom he had worked in emergency rooms all over Knoxville — including the one where she died. That day three years ago still makes no sense to him.
"She was very strong-willed, strong-minded, an independent, young, female physician," says emergency doctor Betsy Hull, a close friend. "I don't think any of us had any idea that she was struggling as much personally as she was for those several months."
That day she became part of a grim set of statistics.
A harsh reality
An estimated 300 to 400 doctors kill themselves each year, a rate of 28 to 40 per 100,000 or more than double that of general population. That is according to a review of 10 years of literature on the subject presented at the American Psychiatry Association annual meeting in May.
The information is here.
Tuesday, August 28, 2018
As calls to the Suicide Prevention Lifeline surge, under-resourced centers struggle to keep up
Vivekae Kim
PBS.org
Originally posted August 5, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
To accommodate the rising call volume, Dr. Draper, the director of the Lifeline, says local crisis centers need more resources–and that a lack of resources contributes to centers leaving the network or shutting down. From 2008-2012, nine centers dropped out of the network and from 2013-2017, 23 centers dropped out. Just this year, three centers shut down.
Remaining centers do what they can to stay functioning. This often means taking on extra contracts, like running local crisis lines, to support their suicide prevention work.
Crisis Call Center, a Lifeline backup center in Nevada, operates a sexual assault support service program and a substance abuse hotline. They also provide child protective service reports and take elder protective service reports after hours. Rachelle Pellissier, its executive director, says they have to “cobble together” these different funding streams to offset the costs of the suicide prevention calls they take.
“We really need about $1.1 million to run this organization,” said Pellissier.
Centers like Provident in Missouri rely on their local United Way. The money they receive from the Lifeline, even as a backup center with more support, “pays for maybe two salaries of my 15 person team,” said Jane Smith, the director of life crisis services for Provident. “We’re a money-losing entity at Provident.”
If backup centers are unable to take a call, that call is routed from one backup center to the next, until a counselor can talk. “All the calls can be answered. The only question is, how long do people wait?” Draper said.
The info is here.
PBS.org
Originally posted August 5, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
To accommodate the rising call volume, Dr. Draper, the director of the Lifeline, says local crisis centers need more resources–and that a lack of resources contributes to centers leaving the network or shutting down. From 2008-2012, nine centers dropped out of the network and from 2013-2017, 23 centers dropped out. Just this year, three centers shut down.
Remaining centers do what they can to stay functioning. This often means taking on extra contracts, like running local crisis lines, to support their suicide prevention work.
Crisis Call Center, a Lifeline backup center in Nevada, operates a sexual assault support service program and a substance abuse hotline. They also provide child protective service reports and take elder protective service reports after hours. Rachelle Pellissier, its executive director, says they have to “cobble together” these different funding streams to offset the costs of the suicide prevention calls they take.
“We really need about $1.1 million to run this organization,” said Pellissier.
Centers like Provident in Missouri rely on their local United Way. The money they receive from the Lifeline, even as a backup center with more support, “pays for maybe two salaries of my 15 person team,” said Jane Smith, the director of life crisis services for Provident. “We’re a money-losing entity at Provident.”
If backup centers are unable to take a call, that call is routed from one backup center to the next, until a counselor can talk. “All the calls can be answered. The only question is, how long do people wait?” Draper said.
The info is here.
Thursday, August 9, 2018
Why is suicide on the rise in the US – but falling in most of Europe?
 Steven Stack
Steven StackThe Conversation
Originally published June 28, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
There is evidence that rising suicide rates are associated with a weakening of the social norms regarding mutual aid and support.
In one study on suicide in the U.S., the rising rates were closely linked with reductions in social welfare spending between 1960 and 1995. Social welfare expenditures include Medicaid, a medical assistance program for low income persons; Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, which replaced Aid to Families with Dependent Children; the Supplemental Security Income program for the blind, disabled and elderly; children’s services including adoption, foster care and day care; shelters; and funding of public hospitals for medical assistance other than Medicaid.
Later studies found a similar relationship between suicide and social welfare for the U.S. in the 1980s and between 1990 and 2000, as well as for nations in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Economic Development.
When it comes to spending on social welfare, the U.S. is at the low end of the spectrum relative to Western Europe. For example, only 18.8 percent of the U.S. GDP is spent on social welfare, while most of the OECD nations spend at least 25 percent of their GDP. Our rates of suicide are increasing while their rates fall.
The information is here.
Wednesday, July 18, 2018
Why are Americans so sad?
Monica H. Swahn
quartz.com
Originally published June 16, 2018
Suicide rates in the US have increased nearly 30% in less than 20 years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported June 7. These mind-numbing statistics were released the same week two very famous, successful and beloved people committed suicide—Kate Spade, a tremendous entrepreneur, trendsetter and fashion icon, and Anthony Bourdain, a distinguished chef and world traveler who took us on gastronomic journeys to all corners of the world through his TV shows.
Their tragic deaths, and others like them, have brought new awareness to the rapidly growing public health problem of suicide in the US. These deaths have renewed the country’s conversation about the scope of the problem. The sad truth is that suicide is the 10th leading cause of death among all Americans, and among youth and young adults, suicide is the third leading cause of death.
I believe it’s time for us to pause and to ask the question why? Why are the suicide rates increasing so fast? And, are the increasing suicide rates linked to the seeming increase in demand for drugs such as marijuana, opioids and psychiatric medicine? As a public health researcher and epidemiologist who has studied these issues for a long time, I think there may be deeper issues to explore.
Suicide: more than a mental health issue
Suicide prevention is usually focused on the individual and within the context of mental health illness, which is a very limited approach. Typically, suicide is described as an outcome of depression, anxiety, and other mental health concerns including substance use. And, these should not be trivialized; these conditions can be debilitating and life-threatening and should receive treatment. (If you or someone you know need help, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255).
The info is here.
quartz.com
Originally published June 16, 2018
Suicide rates in the US have increased nearly 30% in less than 20 years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported June 7. These mind-numbing statistics were released the same week two very famous, successful and beloved people committed suicide—Kate Spade, a tremendous entrepreneur, trendsetter and fashion icon, and Anthony Bourdain, a distinguished chef and world traveler who took us on gastronomic journeys to all corners of the world through his TV shows.
Their tragic deaths, and others like them, have brought new awareness to the rapidly growing public health problem of suicide in the US. These deaths have renewed the country’s conversation about the scope of the problem. The sad truth is that suicide is the 10th leading cause of death among all Americans, and among youth and young adults, suicide is the third leading cause of death.
I believe it’s time for us to pause and to ask the question why? Why are the suicide rates increasing so fast? And, are the increasing suicide rates linked to the seeming increase in demand for drugs such as marijuana, opioids and psychiatric medicine? As a public health researcher and epidemiologist who has studied these issues for a long time, I think there may be deeper issues to explore.
Suicide: more than a mental health issue
Suicide prevention is usually focused on the individual and within the context of mental health illness, which is a very limited approach. Typically, suicide is described as an outcome of depression, anxiety, and other mental health concerns including substance use. And, these should not be trivialized; these conditions can be debilitating and life-threatening and should receive treatment. (If you or someone you know need help, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255).
The info is here.
Saturday, June 2, 2018
Preventing Med School Suicides
Roger Sergel
MegPage Today
Originally posted May 2, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
The medical education community needs to acknowledge the stress imposed on our medical learners as they progress from students to faculty. One of the biggest obstacles is changing the culture of medicine to not only understand the key burnout drivers and pain points but to invest resources into developing strategies which reduce stress. These strategies must include the medical learner taking ownership for the role they play in their lack of well-being. In addition, medical schools and healthcare organizations must reflect on their policies/processes which do not promote wellness. In both situations, there is pointing to the other group as the one who needs to change. Both are right.
We do need to change how we deliver a quality medical education AND we need our medical learners to reflect on their personal attitudes and openness to developing their resilience muscles to manage their stress. Equally important, we need to reduce the stigma of seeking help and break down the barriers which would allow our medical learners and physicians to seek help, when needed. We need to create support services which are convenient, accessible, and utilized.
What programs does your school have to support medical students' mental health?
The information is here.
MegPage Today
Originally posted May 2, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
The medical education community needs to acknowledge the stress imposed on our medical learners as they progress from students to faculty. One of the biggest obstacles is changing the culture of medicine to not only understand the key burnout drivers and pain points but to invest resources into developing strategies which reduce stress. These strategies must include the medical learner taking ownership for the role they play in their lack of well-being. In addition, medical schools and healthcare organizations must reflect on their policies/processes which do not promote wellness. In both situations, there is pointing to the other group as the one who needs to change. Both are right.
We do need to change how we deliver a quality medical education AND we need our medical learners to reflect on their personal attitudes and openness to developing their resilience muscles to manage their stress. Equally important, we need to reduce the stigma of seeking help and break down the barriers which would allow our medical learners and physicians to seek help, when needed. We need to create support services which are convenient, accessible, and utilized.
What programs does your school have to support medical students' mental health?
The information is here.
Monday, May 28, 2018
This Suicide Pod Dubbed 'the Tesla of Death' Lets You Kill Yourself Peacefully
Loukia Papadopoulos
Interesting Engineering
Originally posted April 27, 2018
 A new controversial pod for ending one’s life is on the market and it is being dubbed the Tesla of death and its founder, the Elon Musk of suicide. The pod, developed by euthanasia campaigner Dr. Philip Nitschke, is called the Sarco and it seeks to revolutionize the way we die.
A new controversial pod for ending one’s life is on the market and it is being dubbed the Tesla of death and its founder, the Elon Musk of suicide. The pod, developed by euthanasia campaigner Dr. Philip Nitschke, is called the Sarco and it seeks to revolutionize the way we die.
The Sarco's website features a thought-provoking question on its landing page. “What if we had more than mere dignity to look forward to on our last day on this planet?” reads the site.
A description of the pod goes on to explain that “the elegant design was intended to suggest a sense of occasion: of travel to a ‘new destination’, and to dispel the ‘yuk’ factor.” If this sounds like a macabre joke, rest assured it is not.
The article is here.
Interesting Engineering
Originally posted April 27, 2018
 A new controversial pod for ending one’s life is on the market and it is being dubbed the Tesla of death and its founder, the Elon Musk of suicide. The pod, developed by euthanasia campaigner Dr. Philip Nitschke, is called the Sarco and it seeks to revolutionize the way we die.
A new controversial pod for ending one’s life is on the market and it is being dubbed the Tesla of death and its founder, the Elon Musk of suicide. The pod, developed by euthanasia campaigner Dr. Philip Nitschke, is called the Sarco and it seeks to revolutionize the way we die.The Sarco's website features a thought-provoking question on its landing page. “What if we had more than mere dignity to look forward to on our last day on this planet?” reads the site.
A description of the pod goes on to explain that “the elegant design was intended to suggest a sense of occasion: of travel to a ‘new destination’, and to dispel the ‘yuk’ factor.” If this sounds like a macabre joke, rest assured it is not.
The article is here.
Tuesday, May 22, 2018
Truckers Line Up Under Bridge To Save Man Threatening Suicide
Vanessa Romo
 www.npr.org
www.npr.org
Originally published April 24, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
"It provides a safety net for the person in case they happen to lose their grip and fall or if they decide to jump," Shaw said. "With the trucks lined up underneath they're only falling about five to six feet as opposed 15 or 16."
After about two hours of engaging with officials the distressed man willingly backed off the edge and is receiving help, Shaw said.
"He was looking to take his own life but we were able to talk to him and find out what his specific trigger was and helped correct it," Shaw said.
In all, the ordeal lasted about three hours.
The article is here.
 www.npr.org
www.npr.orgOriginally published April 24, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
"It provides a safety net for the person in case they happen to lose their grip and fall or if they decide to jump," Shaw said. "With the trucks lined up underneath they're only falling about five to six feet as opposed 15 or 16."
After about two hours of engaging with officials the distressed man willingly backed off the edge and is receiving help, Shaw said.
"He was looking to take his own life but we were able to talk to him and find out what his specific trigger was and helped correct it," Shaw said.
In all, the ordeal lasted about three hours.
The article is here.
Wednesday, March 21, 2018
Suicidal Ideation, Plans, and Attempts Among Public Safety Personnel in Canada
R. N. Carleton and others
Canadian Psychology
First published February 8, 2018
Abstract
Substantial media attention has focused on suicide among Canadian Public Safety Personnel (PSP; e.g., correctional workers, dispatchers, firefighters, paramedics, police). The attention has raised significant concerns about the mental health impact of public safety service, as well as interest in the correlates for risk of suicide. There have only been two published studies assessing lifetime suicidal behaviors among Canadian PSP. The current study was designed to assess past-year and lifetime suicidal ideation, plans, and attempts amongst a large diverse sample of Canadian PSP. Estimates of suicidal ideation, plans, and attempts were derived from self-reported data from a nationally administered online survey. Participants included 5,148 PSP (33.4% women) grouped into six categories (i.e., Call Centre Operators/Dispatchers, Correctional Workers, Firefighters, Municipal/Provincial Police, Paramedics, Royal Canadian Mounted Police). Substantial proportions of participants reported past-year and lifetime suicidal ideation (10.1%, 27.8%), planning (4.1%, 13.3%), or attempts (0.4%, 4.6%). Women reported significantly more lifetime suicidal behaviors than men (ORs = 1.15 to 2.62). Significant differences were identified across PSP categories in reports of past-year and lifetime suicidal behaviors. The proportion of Canadian PSP reporting past-year and lifetime suicidal behaviors was substantial. The estimates for lifetime suicidal behaviors appear consistent with or higher than previously published international PSP estimates, and higher than reports from the general population. Municipal/Provincial Police reported the lowest frequency for past-year and lifetime suicidal behaviors, whereas Correctional Workers and Paramedics reported the highest. The results provide initial evidence that substantial portions of diverse Canadian PSP experience suicidal behaviors, therein warranting additional resources and research.
The research is here.
Canadian Psychology
First published February 8, 2018
Abstract
Substantial media attention has focused on suicide among Canadian Public Safety Personnel (PSP; e.g., correctional workers, dispatchers, firefighters, paramedics, police). The attention has raised significant concerns about the mental health impact of public safety service, as well as interest in the correlates for risk of suicide. There have only been two published studies assessing lifetime suicidal behaviors among Canadian PSP. The current study was designed to assess past-year and lifetime suicidal ideation, plans, and attempts amongst a large diverse sample of Canadian PSP. Estimates of suicidal ideation, plans, and attempts were derived from self-reported data from a nationally administered online survey. Participants included 5,148 PSP (33.4% women) grouped into six categories (i.e., Call Centre Operators/Dispatchers, Correctional Workers, Firefighters, Municipal/Provincial Police, Paramedics, Royal Canadian Mounted Police). Substantial proportions of participants reported past-year and lifetime suicidal ideation (10.1%, 27.8%), planning (4.1%, 13.3%), or attempts (0.4%, 4.6%). Women reported significantly more lifetime suicidal behaviors than men (ORs = 1.15 to 2.62). Significant differences were identified across PSP categories in reports of past-year and lifetime suicidal behaviors. The proportion of Canadian PSP reporting past-year and lifetime suicidal behaviors was substantial. The estimates for lifetime suicidal behaviors appear consistent with or higher than previously published international PSP estimates, and higher than reports from the general population. Municipal/Provincial Police reported the lowest frequency for past-year and lifetime suicidal behaviors, whereas Correctional Workers and Paramedics reported the highest. The results provide initial evidence that substantial portions of diverse Canadian PSP experience suicidal behaviors, therein warranting additional resources and research.
The research is here.
Thursday, March 8, 2018
More Religious Leaders Challenge Silence, Isolation Surrounding Suicide
Cheryl Platzman Weinstock
npr.org
Originally posted February 11, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Until recently, many religious leaders were not well-prepared to talk about suicide with their congregants. Now some clergy have become an important part of suicide prevention.
"Where there's faith, there's hope, and where there's hope, there's life," says David Litts, co-leader of the Faith Communities Task Force of the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention.
Arnold also leads that task force. "If someone dies from heart disease, for instance, or in an accident, they may wonder where God is, but when someone dies by suicide, a whole lot of other questions get raised," she says. "When you can't talk about this in church, then it feels like God can't talk about it either."
But in her church, she says, there isn't shame surrounding suicide. During the pastoral prayer, for instance, she says she lifts up congregants dealing with cancer, heart disease or mental health issues. "It's a way of signaling to people this is a safe place to talk about such things and be honest about them."
The article is here.
npr.org
Originally posted February 11, 2018
Here is an excerpt:
Until recently, many religious leaders were not well-prepared to talk about suicide with their congregants. Now some clergy have become an important part of suicide prevention.
"Where there's faith, there's hope, and where there's hope, there's life," says David Litts, co-leader of the Faith Communities Task Force of the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention.
Arnold also leads that task force. "If someone dies from heart disease, for instance, or in an accident, they may wonder where God is, but when someone dies by suicide, a whole lot of other questions get raised," she says. "When you can't talk about this in church, then it feels like God can't talk about it either."
But in her church, she says, there isn't shame surrounding suicide. During the pastoral prayer, for instance, she says she lifts up congregants dealing with cancer, heart disease or mental health issues. "It's a way of signaling to people this is a safe place to talk about such things and be honest about them."
The article is here.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)