By Sarah Graham
The Independent
Originally posted October 17, 2015
Here is an excerpt:
It’s not surprising so many people are ignorant about us intersex people: Our very existence has been erased since the Roman Empire. It continued in the 20th century, as doctors got their scalpels out to “normalise” our bodies. In the last fifteen years, since some of us started finding our dissident voices and protesting, doctors have tried to rebrand us and said we have “Disorders of Sexual Development (DSDs)” - to legitimize their paternalism and on-going annihilation of our beings.
This is all to keep you - the public - in the dark. And to rigidly enforce the pink and blue boxes: the boring binary, straight-laced order. But let me bring you up-to-speed. There are not only the two sexes of male and female. This is an absolute barefaced lie. Nature produces bodies on a spectrum; a continuum of possibilities.
You have met one of us somewhere, for sure. As many as 1 in 1,500 babies is born visibly intersex, while many more are born not so obviously unique and interesting to the eye.
The entire article is here.
Welcome to the Nexus of Ethics, Psychology, Morality, Philosophy and Health Care
Welcome to the nexus of ethics, psychology, morality, technology, health care, and philosophy
Showing posts with label Gender. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Gender. Show all posts
Wednesday, November 4, 2015
Friday, April 24, 2015
Gender Differences in Responses to Moral Dilemmas
By Rebecca Riesdorf, Paul Conway, and Bertram Gawronski
Pers Soc Psychol Bull April 3, 2015
Abstract
The principle of deontology states that the morality of an action depends on its consistency with moral norms; the principle of utilitarianism implies that the morality of an action depends on its consequences. Previous research suggests that deontological judgments are shaped by affective processes, whereas utilitarian judgments are guided by cognitive processes. The current research used process dissociation (PD) to independently assess deontological and utilitarian inclinations in women and men. A meta-analytic re-analysis of 40 studies with 6,100 participants indicated that men showed a stronger preference for utilitarian over deontological judgments than women when the two principles implied conflicting decisions (d = 0.52). PD further revealed that women exhibited stronger deontological inclinations than men (d = 0.57), while men exhibited only slightly stronger utilitarian inclinations than women (d = 0.10). The findings suggest that gender differences in moral dilemma judgments are due to differences in affective responses to harm rather than cognitive evaluations of outcomes.
The entire article is here.
Pers Soc Psychol Bull April 3, 2015
Abstract
The principle of deontology states that the morality of an action depends on its consistency with moral norms; the principle of utilitarianism implies that the morality of an action depends on its consequences. Previous research suggests that deontological judgments are shaped by affective processes, whereas utilitarian judgments are guided by cognitive processes. The current research used process dissociation (PD) to independently assess deontological and utilitarian inclinations in women and men. A meta-analytic re-analysis of 40 studies with 6,100 participants indicated that men showed a stronger preference for utilitarian over deontological judgments than women when the two principles implied conflicting decisions (d = 0.52). PD further revealed that women exhibited stronger deontological inclinations than men (d = 0.57), while men exhibited only slightly stronger utilitarian inclinations than women (d = 0.10). The findings suggest that gender differences in moral dilemma judgments are due to differences in affective responses to harm rather than cognitive evaluations of outcomes.
The entire article is here.
Friday, September 26, 2014
Females ignored in basic medical research
By Erin White
Science Daily
Published August 28, 2014
A new study from Northwestern Medicine® has found that surgical researchers rarely use female animals or female cells in their published studies -- despite a huge body of evidence showing that sex differences can play a crucial role in medical research.
Editors of the five major surgical journals reviewed in this study have responded to this finding and will now require authors to state the sex of animals and cells used in their studies. If they use only one sex in their studies, they will be asked to justify why.
The entire article is here.
Science Daily
Published August 28, 2014
A new study from Northwestern Medicine® has found that surgical researchers rarely use female animals or female cells in their published studies -- despite a huge body of evidence showing that sex differences can play a crucial role in medical research.
Editors of the five major surgical journals reviewed in this study have responded to this finding and will now require authors to state the sex of animals and cells used in their studies. If they use only one sex in their studies, they will be asked to justify why.
The entire article is here.
Thursday, July 24, 2014
‘She’s not a slag because she only had sex once’: Sexual ethics in a London secondary school
By Sarah Winkler Reid
Journal of Moral Education
Volume 43, Issue 2, 2014
Special Issue: ‘The good child’: Anthropological perspectives on morality and childhood
Abstract
The premature sexualisation of young people is a source of intense public anxiety, often framed as an unprecedented crisis. Concurrently, a critical scholarship highlights problematic assumptions underpinning this discourse, including a positioning of young people as morally compromised passive subjects, and a disconnect between the reductionist framework and the complexity of young peoples’ lived experiences. Drawing from ethnographic research in a London school, in this article I argue that by attending to the everyday lives of pupils, a more nuanced picture of moral and sexual change and continuity emerges. Using the framework of ‘ordinary ethics’, which identifies ethics as pervasive in speech and action, I demonstrate the multiple ways by which young people define and act according to what they consider sexually good and right. In this way the analytical focus is shifted from passivity to activity and we can appreciate how young people today are evincing a sexual ethics of force and efficacy.
The entire article is here.
Journal of Moral Education
Volume 43, Issue 2, 2014
Special Issue: ‘The good child’: Anthropological perspectives on morality and childhood
Abstract
The premature sexualisation of young people is a source of intense public anxiety, often framed as an unprecedented crisis. Concurrently, a critical scholarship highlights problematic assumptions underpinning this discourse, including a positioning of young people as morally compromised passive subjects, and a disconnect between the reductionist framework and the complexity of young peoples’ lived experiences. Drawing from ethnographic research in a London school, in this article I argue that by attending to the everyday lives of pupils, a more nuanced picture of moral and sexual change and continuity emerges. Using the framework of ‘ordinary ethics’, which identifies ethics as pervasive in speech and action, I demonstrate the multiple ways by which young people define and act according to what they consider sexually good and right. In this way the analytical focus is shifted from passivity to activity and we can appreciate how young people today are evincing a sexual ethics of force and efficacy.
The entire article is here.
Sunday, May 25, 2014
What Happens Before? A Field Experiment Exploring How Pay and Representation Differentially Shape Bias on the Pathway into Organizations
By Katherine Milkman, Modupe Akinola, and Dolly Chugh
Originally posted April 23, 2014
Abstract:
Little is known about how bias against women and minorities varies within and between organizations or how it manifests before individuals formally apply to organizations. We address this knowledge gap through an audit study in academia of over 6,500 professors at top U.S. universities drawn from 89 disciplines and 259 institutions. We hypothesized that discrimination would appear at the informal “pathway” preceding entry to academia and would vary by discipline and university as a function of faculty representation and pay. In our experiment, professors were contacted by fictional prospective students seeking to discuss research opportunities prior to applying to a doctoral program. Names of students were randomly assigned to signal gender and race (Caucasian, Black, Hispanic, Indian, Chinese), but messages were otherwise identical. We found that faculty ignored requests from women and minorities at a higher rate than requests from White males, particularly in higher-paying disciplines and private institutions. Counterintuitively, the representation of women and minorities and bias were uncorrelated, suggesting that greater representation cannot be assumed to reduce bias. This research highlights the importance of studying what happens before formal entry points into organizations and reveals that discrimination is not evenly distributed within and between organizations.
The entire research paper is here.
Originally posted April 23, 2014
Abstract:
Little is known about how bias against women and minorities varies within and between organizations or how it manifests before individuals formally apply to organizations. We address this knowledge gap through an audit study in academia of over 6,500 professors at top U.S. universities drawn from 89 disciplines and 259 institutions. We hypothesized that discrimination would appear at the informal “pathway” preceding entry to academia and would vary by discipline and university as a function of faculty representation and pay. In our experiment, professors were contacted by fictional prospective students seeking to discuss research opportunities prior to applying to a doctoral program. Names of students were randomly assigned to signal gender and race (Caucasian, Black, Hispanic, Indian, Chinese), but messages were otherwise identical. We found that faculty ignored requests from women and minorities at a higher rate than requests from White males, particularly in higher-paying disciplines and private institutions. Counterintuitively, the representation of women and minorities and bias were uncorrelated, suggesting that greater representation cannot be assumed to reduce bias. This research highlights the importance of studying what happens before formal entry points into organizations and reveals that discrimination is not evenly distributed within and between organizations.
The entire research paper is here.
Saturday, November 9, 2013
Suicide Rate Climbs by 30 Percent in Kansas as Government Slashes Mental Health Budgets
Allison Kilkenny
on October 21, 2013
The Nation
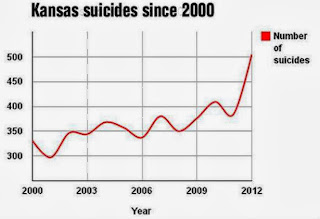 The Kansas
Department of Health and Environment recently released a startling report (PDF) showing
a 30 percent increase in suicides from 2011. Nationwide, the number of deaths
by suicide surpassed
the number of deaths by motor vehicle accidents in 2009, the
most recent year for which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
provided data.
The Kansas
Department of Health and Environment recently released a startling report (PDF) showing
a 30 percent increase in suicides from 2011. Nationwide, the number of deaths
by suicide surpassed
the number of deaths by motor vehicle accidents in 2009, the
most recent year for which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
provided data.The Wichita Eagle reports that the largest increase in suicides in Kansas occurred among white males, who already were the segment of the population most likely to take their own lives. More than 80 percent of suicides in Kansas last year were men, like Scott Dennis, a 42-year-old fitness company owner.
Tuesday, October 1, 2013
"Fairer Sex" or Purity Myth? Corruption, Gender, and Institutional Context
By Justin Esarey and Gina Chirillo
Abstract
Cross-national studies have found evidence that women are individually more disapproving of corruption than men, and that female participation in government is negatively associated with perceived corruption at the country level. In this paper, we argue that this difference reflects greater pressure on women to comply with political norms as a result of discrimination and risk aversion, and therefore a gender gap exists in some political contexts but not others. Bribery, favoritism, and personal loyalty are often characteristic of the normal operation of autocratic governments and not stigmatized as corruption; we nd weak or non-existent relationships between gender and corruption in this context. We find much stronger relationships in democracies, where corruption is more typically stigmatized.
The entire paper is here.
Abstract
Cross-national studies have found evidence that women are individually more disapproving of corruption than men, and that female participation in government is negatively associated with perceived corruption at the country level. In this paper, we argue that this difference reflects greater pressure on women to comply with political norms as a result of discrimination and risk aversion, and therefore a gender gap exists in some political contexts but not others. Bribery, favoritism, and personal loyalty are often characteristic of the normal operation of autocratic governments and not stigmatized as corruption; we nd weak or non-existent relationships between gender and corruption in this context. We find much stronger relationships in democracies, where corruption is more typically stigmatized.
The entire paper is here.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)